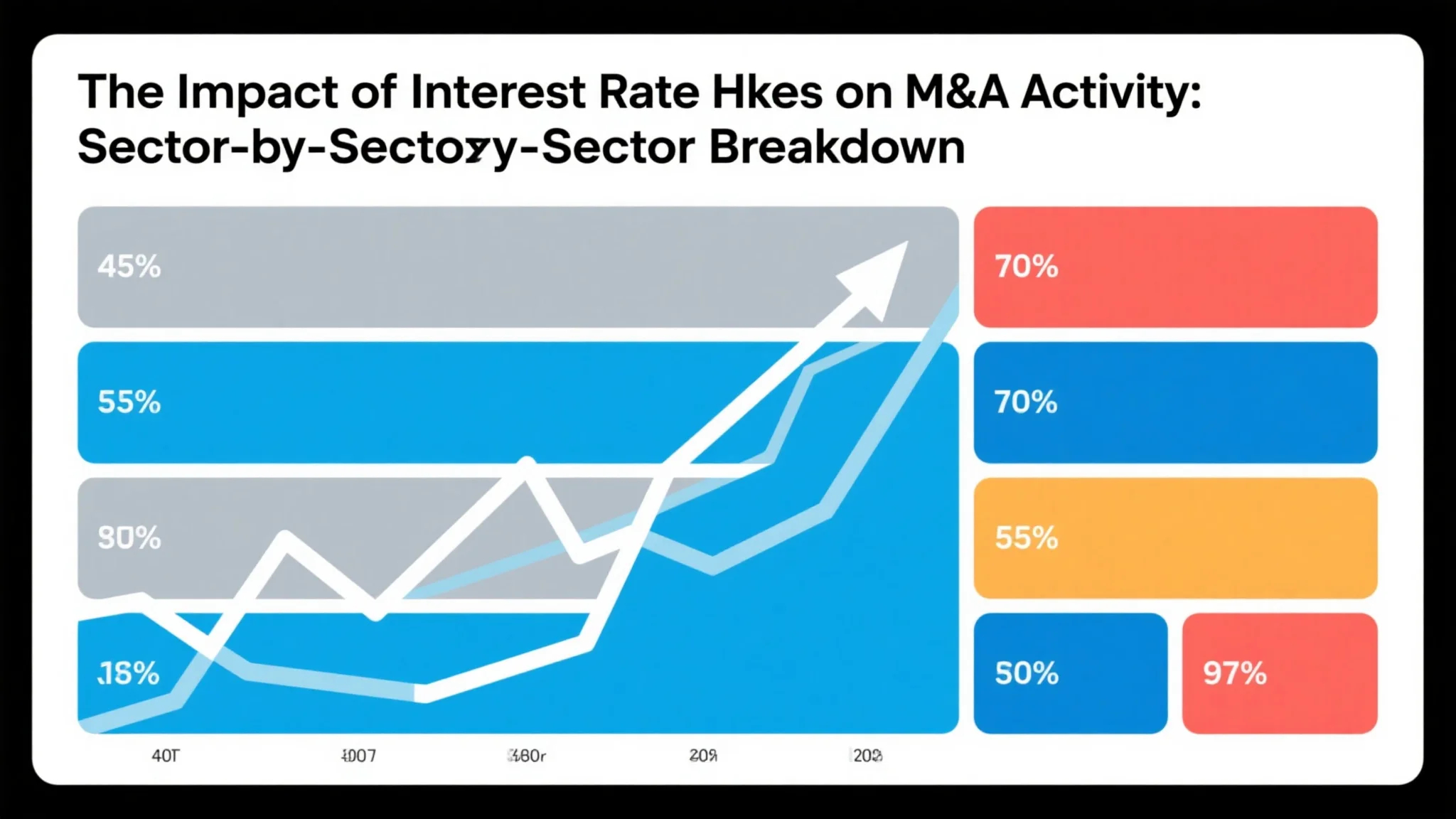
The relationship between interest rates and mergers and acquisitions activity represents one of the most significant macroeconomic factors influencing corporate strategic decisions, with rising borrowing costs fundamentally altering the financial calculus that drives deal-making across virtually every industry sector. When central banks implement monetary tightening policies, the ripple effects extend far beyond traditional lending markets, creating a complex web of consequences that reshape how companies approach growth strategies, capital allocation decisions, and competitive positioning initiatives. The interest rate M&A impact manifests through multiple channels, including increased financing costs for leveraged transactions, higher discount rates that reduce present values of future cash flows, and shifting investor preferences that favor immediate returns over long-term growth investments. These macroeconomic shifts force corporate executives and private equity professionals to recalibrate their acquisition strategies, often leading to more selective deal-making processes, enhanced focus on operational improvements rather than financial engineering, and increased emphasis on transactions that can generate immediate synergies or cost savings. The complexity of these dynamics becomes particularly pronounced when examining how different industry sectors respond to interest rate changes, as each sector’s unique characteristics—including capital intensity, growth profiles, regulatory environments, and competitive structures—create distinct patterns of M&A activity adaptation. Technology companies, for instance, may find their high-growth, future-cash-flow-dependent valuations particularly sensitive to discount rate changes, while utility companies with stable, predictable cash flows might experience relatively modest valuation impacts despite higher borrowing costs. Understanding these sector-specific responses requires careful analysis of how interest rate changes interact with industry fundamentals, competitive dynamics, and strategic imperatives that drive consolidation activity. The timing and magnitude of interest rate adjustments also play crucial roles in determining M&A market responses, with gradual, well-telegraphed increases often allowing markets to adapt more smoothly than sudden, dramatic policy shifts that can create significant uncertainty and transaction delays.
Financial Services and Real Estate: Navigating the Direct Impact of Monetary Policy
The financial services and real estate sectors experience the most immediate and pronounced effects of interest rate changes, given their fundamental dependence on borrowing costs, lending spreads, and asset valuations that directly correlate with monetary policy decisions. Banks and other financial institutions face a complex set of challenges and opportunities when interest rates rise, as higher rates can improve net interest margins for traditional lending businesses while simultaneously reducing the present value of loan portfolios and increasing credit risk concerns. The sector M&A analysis reveals that financial services consolidation often accelerates during periods of rising rates, as smaller institutions seek the protection and resources of larger partners to navigate challenging operating environments. Regional banks, in particular, may find themselves under pressure from compressed margins, increased regulatory scrutiny, and the need for significant technology investments that favor scale economies achievable through strategic combinations. The real estate sector faces even more direct impacts from interest rate increases, as property valuations depend heavily on capitalization rates and financing availability that deteriorate as borrowing costs rise. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) often experience significant valuation pressure during rate hiking cycles, creating opportunities for private equity firms and strategic buyers to acquire assets at discounted prices, though the availability of acquisition financing may simultaneously become more constrained and expensive. Commercial real estate transactions frequently involve complex financing structures that become increasingly challenging to execute as rates rise, leading to longer transaction timelines, more conservative leverage ratios, and greater emphasis on cash-heavy deal structures. Residential real estate companies face additional challenges from reduced consumer demand as mortgage rates increase, creating pressure on homebuilders, mortgage originators, and related service providers that may drive consolidation as companies seek to achieve cost synergies and operational efficiencies. The insurance sector presents a more nuanced picture, as life insurers may benefit from higher investment yields on new money while property and casualty insurers face potential increases in claims costs and reserve requirements that could pressure profitability and drive strategic combinations.
Private equity activity within financial services and real estate sectors demonstrates particularly interesting dynamics during interest rate hiking cycles, as these investors must balance the challenges of higher acquisition financing costs against the opportunities created by sector distress and valuation compression. Financial services private equity transactions often focus on specialty finance companies, fintech platforms, and niche lending businesses that can benefit from operational improvements and technology investments that larger financial institutions may struggle to implement efficiently. The due diligence processes for these transactions become increasingly rigorous during periods of monetary tightening, with enhanced focus on asset quality, interest rate sensitivity analysis, and stress testing scenarios that examine performance under various economic conditions. Real estate private equity strategies frequently shift toward value-add and opportunistic investments that can benefit from operational improvements, repositioning strategies, and market timing advantages that become more pronounced during periods of market dislocation. The availability of debt financing for these transactions often becomes a critical constraint, leading to more conservative leverage ratios, higher equity contributions, and creative financing structures that may include seller financing, earnout provisions, or staged acquisition approaches. Cross-border transactions in these sectors face additional complexity from currency hedging considerations and regulatory differences that can create both opportunities and challenges for international investors seeking to capitalize on interest rate-driven market dislocations. The regulatory environment for financial services M&A often becomes more scrutinized during periods of economic uncertainty, with regulators paying increased attention to systemic risk considerations, capital adequacy requirements, and competitive effects that may influence approval timelines and transaction structures. Real estate transactions may face additional regulatory hurdles related to foreign investment restrictions, environmental compliance requirements, and local zoning or development approval processes that can create execution risk and timeline uncertainty.
Technology and Healthcare: Growth Sector Adaptations to Higher Discount Rates

Technology and healthcare sectors, traditionally characterized by high growth expectations and future cash flow-dependent valuations, face unique challenges during interest rate hiking cycles that fundamentally alter their M&A landscapes and strategic decision-making processes. Technology companies, particularly those in high-growth segments such as software-as-a-service, artificial intelligence, and emerging technology platforms, often experience significant valuation compression as higher discount rates reduce the present value of their projected future cash flows. This valuation pressure creates both challenges and opportunities within the M&A market, as strategic buyers may find acquisition targets more attractively priced while simultaneously facing their own valuation pressures that constrain their acquisition capacity. The M&A activity rates in technology sectors often exhibit increased volatility during periods of monetary tightening, with transaction volumes potentially declining in the near term as buyers and sellers adjust their expectations and valuation methodologies. Private equity investment in technology companies frequently shifts toward more mature, cash-generating businesses that can support higher leverage ratios and provide more predictable returns in higher interest rate environments. Venture capital-backed companies may face particular pressure to achieve profitability or secure strategic exits as the cost of capital increases and investor preferences shift toward businesses with clearer paths to positive cash flow generation. The healthcare sector presents a more complex picture, as different subsectors respond differently to interest rate changes based on their specific business models, regulatory environments, and growth characteristics. Pharmaceutical companies with established product portfolios and predictable cash flows may experience relatively modest valuation impacts, while biotechnology companies dependent on future drug development success may face more significant valuation pressure similar to high-growth technology companies. Healthcare services companies, including hospitals, managed care organizations, and specialty service providers, often benefit from relatively stable demand characteristics that provide some insulation from interest rate impacts, though their acquisition financing costs and expansion strategies may still be affected by monetary policy changes.
The strategic rationale for technology and healthcare M&A transactions often evolves during periods of rising interest rates, with increased emphasis on deals that can generate immediate operational synergies, cost savings, or revenue enhancements rather than purely growth-oriented combinations. Technology companies may focus more heavily on horizontal consolidation that eliminates redundant costs, vertical integration that improves operational efficiency, or acquisitions that provide access to new customer bases or distribution channels with clear revenue synergy potential. The due diligence processes for technology transactions become increasingly focused on sustainable competitive advantages, recurring revenue models, and operational metrics that demonstrate business resilience and cash flow predictability. Healthcare M&A activity often shifts toward transactions that can benefit from regulatory compliance efficiencies, operational scale advantages, or geographic expansion opportunities that provide defensive characteristics against economic uncertainty. Cross-border technology and healthcare transactions face additional complexity from regulatory approval processes, intellectual property transfer requirements, and data privacy compliance considerations that may become more challenging to navigate during periods of economic uncertainty. The financing structures for these transactions frequently require more creative approaches, including contingent value rights, earnout provisions, and staged acquisition mechanisms that help bridge valuation gaps between buyers and sellers while providing downside protection for acquirers. Strategic buyers in these sectors may increasingly favor stock-based transactions that allow them to share valuation risk with target company shareholders while preserving cash for operational investments and organic growth initiatives. Private equity investors often adjust their investment strategies to focus on businesses with stronger defensive characteristics, more predictable cash flows, and clearer paths to operational improvement that can generate returns independent of multiple expansion.
The innovation and competitive dynamics within technology and healthcare sectors create additional considerations for M&A activity during interest rate hiking cycles, as companies must balance the need for strategic positioning against the financial constraints imposed by higher capital costs. Technology companies may accelerate acquisition activity in certain areas to secure competitive advantages or defensive positions before valuations potentially recover, while simultaneously becoming more selective about expansion investments that require significant upfront capital commitments. The healthcare sector’s regulatory environment adds another layer of complexity, as companies must navigate approval processes for transactions while managing the operational challenges of integrating complex organizations under potentially constrained financial conditions. Digital health and health technology companies often find themselves at the intersection of both sector dynamics, facing the valuation pressures common to technology companies while operating within the regulatory and reimbursement frameworks characteristic of healthcare businesses. The international expansion strategies of technology and healthcare companies may be particularly affected by interest rate differentials between countries, currency hedging costs, and the relative attractiveness of different geographic markets for both organic growth and acquisition opportunities. Intellectual property considerations become increasingly important in these sectors during periods of financial constraint, as companies seek to maximize the value of their existing assets while carefully evaluating the strategic importance of potential acquisition targets’ technology portfolios and development pipelines.
Industrial and Consumer Sectors: Operational Focus Amid Financial Constraints
Industrial and consumer-facing sectors demonstrate distinct patterns of M&A adaptation during interest rate hiking cycles, with companies in these traditionally cyclical industries often shifting their strategic focus toward operational efficiency improvements, supply chain optimization, and defensive positioning strategies that can generate value independent of favorable financing conditions. Manufacturing companies across various industrial subsectors frequently experience multiple pressures during periods of monetary tightening, including higher working capital financing costs, increased equipment financing expenses, and potential demand softening as their customers face their own financial constraints. The interest rate M&A impact on industrial companies often manifests through increased focus on horizontal consolidation that can eliminate excess capacity, reduce competitive pressures, and achieve cost synergies through operational improvements and economies of scale. Aerospace and defense companies may find their long-term contract structures provide some insulation from immediate interest rate impacts, though their suppliers and the broader supply chain ecosystem may experience more significant pressures that create consolidation opportunities. Automotive sector M&A activity often reflects the industry’s ongoing transformation toward electric vehicles, autonomous driving technologies, and new mobility services, with interest rate considerations influencing the timing and structure of transactions rather than fundamentally altering strategic imperatives. The capital-intensive nature of many industrial businesses means that acquisition financing becomes a more significant consideration during periods of higher interest rates, often leading to more conservative leverage ratios, increased equity contributions, and greater emphasis on cash flow generation capabilities of target companies. Consumer goods companies face a complex set of challenges during interest rate hiking cycles, as they must navigate potential demand softening from interest-sensitive consumer spending while managing their own financing costs and strategic positioning requirements.
The retail and consumer services sectors exhibit particularly interesting dynamics during periods of monetary tightening, as companies must balance the immediate pressures of higher financing costs against the longer-term strategic imperatives of market share protection and competitive positioning. E-commerce companies and traditional retailers often find their expansion strategies constrained by higher capital costs, leading to increased focus on operational efficiency improvements, supply chain optimization, and strategic partnerships that can provide growth opportunities without requiring significant capital investments. The restaurant and hospitality industries frequently experience both demand-side pressures from reduced consumer discretionary spending and supply-side challenges from higher financing costs for expansion and renovation projects, creating conditions that may favor consolidation among well-capitalized operators. Consumer packaged goods companies often benefit from relatively stable demand characteristics and established distribution relationships that provide some defensive qualities during economic uncertainty, though their acquisition strategies may shift toward brands and businesses that offer immediate operational synergies or access to growing market segments. The sector M&A analysis reveals that consumer-facing companies increasingly prioritize acquisitions that can enhance their digital capabilities, direct-to-consumer channels, and data analytics capabilities that provide competitive advantages independent of macroeconomic conditions. Private equity investment in consumer sectors often focuses on businesses with strong brand recognition, loyal customer bases, and operational improvement opportunities that can generate returns through enhanced efficiency rather than financial engineering. The international expansion strategies of consumer companies may be particularly affected by currency considerations and the relative attractiveness of different geographic markets, with companies potentially accelerating or delaying cross-border transactions based on interest rate differentials and economic conditions in target markets.
Supply chain considerations become increasingly important for industrial and consumer companies during periods of interest rate volatility, as companies seek to optimize their operational footprints, reduce working capital requirements, and enhance their resilience against economic uncertainty through strategic acquisitions and partnerships. Vertical integration strategies may become more attractive as companies seek to reduce their dependence on external suppliers and gain greater control over their cost structures and operational flexibility. The energy sector presents unique dynamics during interest rate hiking cycles, as traditional energy companies may benefit from higher commodity prices and cash flow generation while renewable energy companies face challenges from higher project financing costs and extended payback periods for capital-intensive investments. Chemical companies and other process industries often experience complex interactions between raw material costs, energy expenses, and financing costs that influence their strategic decision-making and acquisition priorities. The logistics and transportation sectors may find their asset-heavy business models particularly sensitive to interest rate changes, creating opportunities for consolidation among companies that can achieve operational synergies and improved asset utilization through strategic combinations. Technology adoption and digital transformation initiatives within industrial and consumer companies may be influenced by interest rate considerations, as companies balance the need for operational improvements against the higher costs of financing these investments. The regulatory environment for industrial and consumer M&A transactions may become more complex during periods of economic uncertainty, with antitrust authorities potentially paying increased attention to market concentration concerns and competitive effects that could influence approval processes and transaction structures. Cross-border transactions in these sectors often involve additional considerations related to trade policies, regulatory differences, and currency hedging strategies that become more complex during periods of interest rate volatility and economic uncertainty.